Table of Contents
Interactive DO-MS App
Installation
This application has been tested on R >= 3.5.0, OSX >= 10.14 / Windows 7/8/10/11. Make sure you have the mos recent version of R and R Studio installed. R can be downloaded from the main R Project page or downloaded with the RStudio Application. All modules are maintained for MaxQuant >= 1.6.0.16.
The application suffers from visual glitches when displayed on unsupported older browsers (such as IE9 commonly packaged with RStudio on Windows). Please use IE >= 11, Firefox, or Chrome for the best user experience.
Running
The easiest way to run the app is directly through RStudio, by opening the DO-MS.Rproj Rproject file
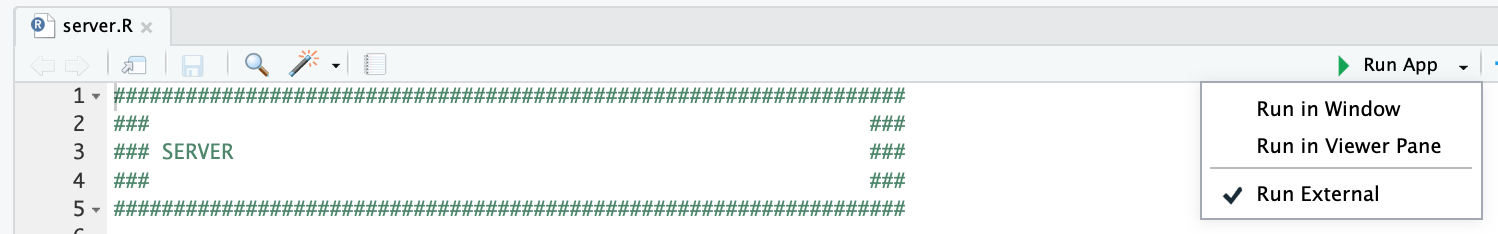
and clicking the “Run App” button at the top of the application, after opening the server.R file. We recommend checking the “Run External” option to open the application in your default browser instead of the RStudio Viewer.
You can also start the application by running the start_server.R script.
More information on using the DO-MS application is provided here.
DIA Python Pipeline
Installation
- Please make sure that Conda or Miniconda are installed.
Use the provided conda configuration to create the environment with all required dependencies.
conda env create -f pipeline/env.yml - Activate the environment and check that the command can be run.
conda activate doms python pipeline/processing.py -h -
For automatic conversion of Thermo Raw files to the open mzML format ThermoRawFileParser (Hulstaert et al. 2020) is required. Download the latest release of the ThermoRawFileParser (version v1.4.0 or newer) and write down the location of the
ThermoRawFileParser.exefile. Under OSX and Linux, Mono. Please make sure to use the option-mwith the feature detection which will tell the script to use Mono. -
For feature detection Dinosaur (Teleman et al. 2016) is used. Download the latest release of the Dinosaur from GitHub and install Java as recommended on your platform. Please write down the location of the
Dinosaur-xx.jarfile. - Optional, create a custom script for your system.
Running
python pipeline/processing.py -h
More information on using the python pipeline is provided here.
Custom Script for Preprocessing
Using the feature detection requires the correct conda environment, ThermoRawFileParser and Dinosaur location. If the tool is used frequently its more convenient to combine the configuration in a script which is added to the system PATH. This will register a local command which can be used everywhere on the system and allows to set default options.
Windows
-
Create a local folder for example under
C:\Users\xxx\Documents\bin. -
Create a file named
processing.batwith the following content. Make sure that all three file paths are changed to the corresponding locations on your system. Further default options can be added to this file if needed. An overview of all command line options can be found here.
@echo off
conda activate doms & ^
python C:\Users\xxx\pipeline\processing.py %* ^
--dinosaur-location "C:\Users\xxx\dinosaur-1.2\Dinosaur-1.2.0.free.jar" ^
--raw-parser-location "C:\Users\xxx\thermo_raw_file_parser_1.3.4\ThermoRawFileParser.exe"
-
Search
environment variablesin the windows search and clickEdit the system environment variables. -
Click
Environment Variablesin the bottom right. -
Select the variable
Pathin the upper panel sayingUser variables ...and clickEdit. -
Click
Newand enter the location of the directory containing theprocessing.batscript. -
Now, the feature processing including the external tools can be called from anywhere on the machine with the
processingcommand.
MacOS
-
Create a local folder for example
/Users/xxx/Documents/bin. - Create a file named
processingwith the following content. Make sure that all three file paths are changed to the corresponding locations on your system.#!/bin/bash eval "$(conda shell.bash hook)" conda activate doms python /Users/xxx/pipeline/processing.py "$@" \ -m \ --dinosaur-location "/Users/xxx/Dinosaur/Dinosaur-1.2.0.free.jar" \ --raw-parser-location "/Users/xxx/ThermoRawFileParser/ThermoRawFileParser.exe"The first line makes conda available to the script (known issue). Please note how the mono option
-mis used by default. Further default options can be added to this file if needed. An overview of all command line options can be found here. -
make the file executable with the following command
chmod +x processing. -
Navigate to the location of your bash profile file in your home directory. This will be
/Users/{username}/.zshrcfor zsh and/Users/{username}/.bash_profilefor bash on macOS and/home/xxx/.bashrcfor bash on linux. Open the file in a text editor of choice, for example vimvim .bash_profile. Go into edit mode by pressingi. -
Add the line
export PATH="/Users/xxx/Documents/bin:$PATH"to the end of the file and save the file by pressingESSC,:wq,Enter. - Restart your terminal.